Mountain Dew Ingredients & Their Nutritional Impact
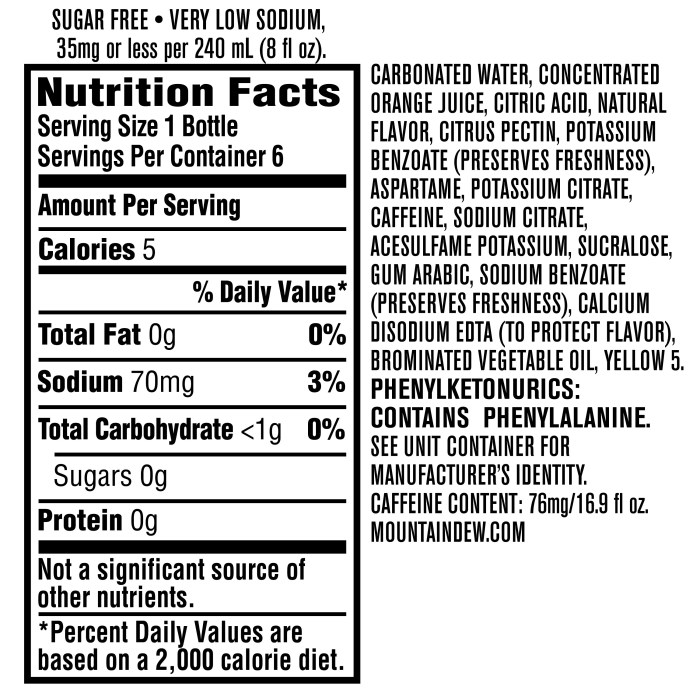
Mountain dew nutrition facts – Mountain Dew, a highly popular carbonated soft drink, boasts a distinct citrus flavor and high caffeine content. However, its nutritional profile is a subject of considerable discussion, largely due to its high sugar content and artificial ingredients. Understanding the ingredients and their individual impacts is crucial for assessing the beverage’s overall health implications.
Ingredient Breakdown and Nutritional Value, Mountain dew nutrition facts
Mountain Dew’s primary ingredients contribute significantly to its taste and overall nutritional (or rather, antinutritional) profile. Carbonated water forms the base, providing fizz. High fructose corn syrup is a major source of sugar, contributing significantly to the drink’s caloric density and potential for weight gain. Citric acid adds tartness, while natural and artificial flavors provide the characteristic citrus taste.
Caffeine provides a stimulant effect. Other ingredients, such as sodium benzoate (a preservative), artificial colors, and other minor additives, further contribute to the final product. The absence of significant vitamins, minerals, or fiber underscores the drink’s lack of nutritional value.
Artificial Sweeteners and Health Implications
While some Mountain Dew variations may utilize artificial sweeteners to reduce sugar content, the long-term health effects of these artificial sweeteners remain a subject of ongoing research and debate. Some studies suggest potential links between artificial sweeteners and metabolic issues, although the evidence is not conclusive and often contradictory. It’s important to note that even “diet” versions of Mountain Dew still contain other potentially less-than-ideal ingredients, and overconsumption of any carbonated beverage can have negative consequences.
Comparison with Similar Carbonated Beverages
Compared to other carbonated beverages, Mountain Dew generally stands out due to its exceptionally high sugar and caffeine content. While other sodas contain similar artificial ingredients and lack nutritional value, Mountain Dew’s specific formulation often results in a higher calorie count and greater potential for adverse health effects if consumed regularly in large quantities. For example, a direct comparison with a typical cola would reveal a similar artificial ingredient profile but a difference in sugar and caffeine levels.
This difference, however, should not be viewed as a significant positive factor, as both beverages are generally not recommended for frequent consumption due to their high sugar and artificial ingredient content.
Mountain Dew Ingredient Analysis
| Ingredient | Quantity (per serving) | Nutritional Value (per serving) | Potential Health Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonated Water | Variable | None | Hydration (but also potential for bloating) |
| High Fructose Corn Syrup | Significant | High in calories, sugars | Weight gain, potential for metabolic issues |
| Citric Acid | Small | None | Adds tartness; generally safe in moderation |
| Caffeine | Moderate to High | Stimulant | Increased alertness, potential for anxiety or insomnia with excessive consumption |
| Artificial Flavors | Variable | None | Potential for allergic reactions; long-term effects are not fully understood |
| Sodium Benzoate | Small | None | Preservative; generally recognized as safe, but some studies suggest potential concerns at high levels |
| Artificial Colors | Small | None | Potential for allergic reactions or hyperactivity in some children (debated) |
Macronutrient Content of Mountain Dew

Mountain Dew, like many other soft drinks, is characterized by a high sugar content and a relatively low presence of other macronutrients like protein and fat. Understanding its macronutrient profile is crucial for assessing its impact on overall health and diet. This analysis will delve into the specific breakdown of carbohydrates, sugars, fats, and protein found in Mountain Dew, comparing it to other popular soft drinks and exploring its potential effects on energy levels and metabolism.
Macronutrient Breakdown of Mountain Dew
A typical 12-ounce serving of Mountain Dew contains approximately 39 grams of carbohydrates, with the vast majority (around 39 grams) coming from sugars. The fat content is negligible, typically less than 0.5 grams per serving. Protein is also virtually absent, usually less than 1 gram per serving. This stark imbalance reflects the drink’s primary role as a source of simple sugars, rather than a contributor to essential nutrients.
Understanding Mountain Dew nutrition facts is crucial for those watching their sugar intake. A direct comparison can be made to the caloric density of other popular fast food items, such as a quarter pounder nutrition facts , which highlights the significant difference in fat content. Returning to Mountain Dew, the high sugar content is a key factor to consider alongside its caffeine level when assessing its overall nutritional profile.
The high sugar content directly translates to a significant number of calories, contributing to potential weight gain if consumed regularly as part of an unbalanced diet.
Proportion of Macronutrients and Daily Recommended Intake
The high sugar content in Mountain Dew significantly impacts daily recommended intakes. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 25 grams per day for women and 36 grams per day for men. A single serving of Mountain Dew already approaches or exceeds these recommendations. The negligible fat and protein content contributes little to the daily recommended values for these macronutrients.
Therefore, relying on Mountain Dew as a source of nutrition is clearly inadequate and potentially detrimental to a balanced diet.
Impact of Mountain Dew Consumption on Energy Levels and Metabolic Processes
The rapid absorption of sugars from Mountain Dew leads to a quick spike in blood glucose levels, followed by a subsequent crash. This rollercoaster effect can result in energy fluctuations, leaving consumers feeling sluggish and craving more sugar later. The high sugar intake can also contribute to insulin resistance over time, potentially increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
The lack of other essential nutrients further exacerbates these negative impacts, leaving the body without the necessary building blocks for optimal functioning.
Comparison of Macronutrient Content with Other Popular Soft Drinks
The following table compares the macronutrient content of Mountain Dew with other popular soft drinks, providing a relative perspective on its nutritional profile. Note that specific values may vary slightly depending on the brand and serving size.
| Soft Drink | Carbohydrates (g) | Sugars (g) | Fat (g) | Protein (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mountain Dew (12 oz) | 39 | 39 | <1 | <1 |
| Coca-Cola (12 oz) | 39 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Pepsi (12 oz) | 41 | 41 | 0 | 0 |
| Sprite (12 oz) | 38 | 38 | 0 | 0 |
Alternative Beverage Choices and Their Nutritional Profiles: Mountain Dew Nutrition Facts
Choosing healthier alternatives to Mountain Dew can significantly improve your overall dietary intake. While Mountain Dew offers a familiar, sweet, and fizzy taste, its high sugar and caffeine content can negatively impact health if consumed regularly. Fortunately, several beverages offer similar satisfying qualities with substantially better nutritional profiles. These alternatives can contribute to a balanced diet and help reduce the intake of added sugars and empty calories.
Many healthier alternatives mimic the crisp, citrusy taste of Mountain Dew while providing essential vitamins, minerals, or antioxidants. These options often feature natural sweeteners, lower sugar content, or are entirely sugar-free, leading to better hydration and overall well-being. By swapping out sugary sodas for these alternatives, individuals can make a noticeable difference in their daily calorie and nutrient intake.
Healthier Beverage Options and Their Nutritional Comparison
The following table compares the nutritional content of Mountain Dew with several healthier alternatives, serving as a guide for informed beverage choices. Note that nutritional values can vary depending on brand and serving size. It’s crucial to always check the specific nutrition label of the product you are purchasing.
| Beverage | Serving Size (oz) | Calories | Sugar (g) | Caffeine (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mountain Dew | 12 | 170 | 46 | 54 |
| Sparkling Water with Lemon & Lime | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unsweetened Iced Tea with Lemon | 12 | 5-10 (depending on brewing method) | 0 | 0-30 (depending on tea type) |
| Flavored Sparkling Water (e.g., La Croix) | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
As the table demonstrates, the healthier alternatives offer significantly fewer calories and substantially less sugar compared to Mountain Dew. While some might contain small amounts of caffeine depending on the ingredients, they generally avoid the high levels found in soda. The absence of added sugars is a major advantage, contributing to better blood sugar control and reducing the risk of weight gain and related health issues.
Contribution to a Balanced Diet
Incorporating these healthier beverage choices into a balanced diet supports overall health and well-being. Replacing sugary drinks like Mountain Dew with options like sparkling water or unsweetened iced tea contributes to better hydration, reduced calorie intake, and improved blood sugar management. These changes can positively impact weight management, energy levels, and overall health outcomes. For example, swapping a daily Mountain Dew for sparkling water could reduce daily sugar intake by 46 grams, a significant reduction in added sugars.
The absence of empty calories also allows for a greater intake of nutrient-rich foods, contributing to a more balanced and healthful diet.
Popular Questions
Does Mountain Dew contain caffeine?
Yes, Mountain Dew contains caffeine, although the exact amount varies slightly depending on the specific product and serving size.
Is Mountain Dew suitable for children?
Due to its high sugar and caffeine content, Mountain Dew is generally not recommended for children. Healthier alternatives are preferable for children’s consumption.
Are there diet versions of Mountain Dew?
Yes, there are diet versions of Mountain Dew that utilize artificial sweeteners to reduce sugar content. However, the long-term health effects of artificial sweeteners are still under investigation.
How does Mountain Dew compare to other energy drinks?
Compared to many energy drinks, Mountain Dew typically has a higher sugar content and a lower concentration of vitamins and minerals. However, it does contain caffeine, which is a common ingredient in energy drinks.
